Recently, the team of Academician Li Lanjuan, Director of the Laboratory, and Professor Cao Hongcui, Director of the Laboratory's biobanking platform, published an important research result in Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences entitled "MSC-derived exosomes attenuate hepatic MSC-derived exosomes attenuate hepatic fibrosis in primary sclerosing cholangitis through inhibition of Th17 differentiation".
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a cholestatic disease characterised by chronic inflammation of the biliary epithelium and periductal fibrosis, in which the patient's biliary immune cells drive hepatic inflammation and fibrosis by affecting the hepatic microenvironment, for which no effective therapeutic agents are available.
Secretion of factors by MSCs in the damaged liver to modulate the immune response and anti-fibrosis has been supported by many data. To address the key scientific question of whether MSC-derived exosomes (ExoMSC) play a therapeutic role in PSC liver fibrosis, this study relied on a biobank and a liver disease research platform, and utilised transcriptomics, multicellular organoid culture technology and basic experiments, combining PSC model mice (Mdr2-/-), PSC patients' liver tissue-derived multicellular organoids, and conducted an in vivo and ex vivo study to investigate the effect of ExoMSC on liver inflammation and fibrosis in PSC. Exploration of the efficacy and mechanism of ExoMSC on PSC liver fibrosis was carried out.
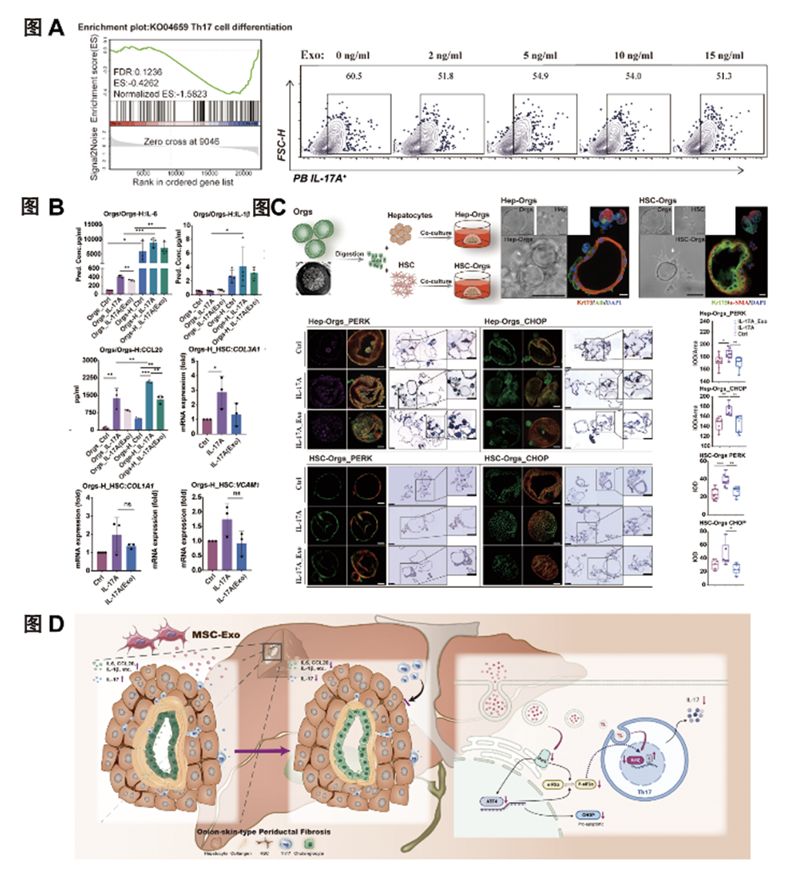
At the molecular, cellular and microenvironmental levels, it was found that ExoMSC inhibited intrahepatic Th17 differentiation in Mdr2-/- mice, and reduced the proportion of Naïve CD4+ T differentiated to CD4+IL17A+ T in vitro (Figure A); improved bile duct hypersecretory phenotypes, hepatic stellate cell activation, and intercellular interactions in the hepatic Th17 microenvironment by modulating PERK/CHOP signalling, and reduced collagen deposition in the hepatic confluent zone (Figure B and C). It was demonstrated that ExoMSC exerted an antifibrotic effect in PSC by inhibiting Th17 differentiation and improving the Th17-induced microenvironment (Figure D), which provided theoretical and data support for the application of ExoMSC in the treatment of liver fibrosis in PSC.
The paper was written by Wenyi Chen as the first author, Prof Hongcui Cao as the corresponding author, and supervised by Academician Lanjuan Li. This research was supported by funds from the National Key Research and Development Programme of China (No. 2020YFA0113003) and the Research Project of Jinan Microecology and Jinan Microecology Biomedical Shandong Laboratory (No. JNL-2022026C and JNL-2023003C).