Research Categories
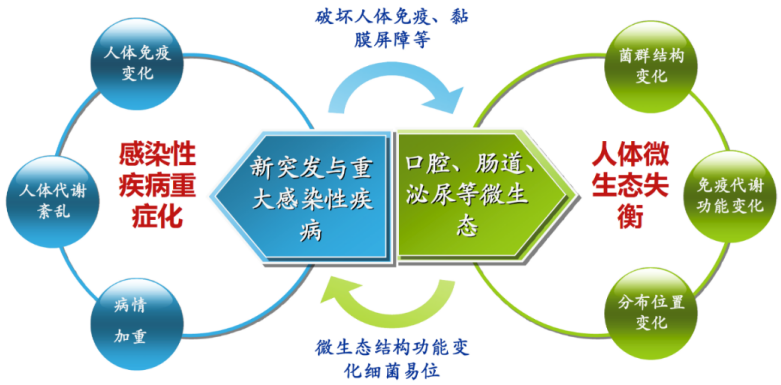
I Human microecology and infectious diseases
The main research topics of human microecology and infectious diseases are as follows: to reveal the interaction signaling pathway between the “inflammatory cytokine storm” of infectious diseases and the microecology; to analyze the interaction between the host susceptibility genes and the human microecology and to explore the impact of the microbiota regulated by the susceptibility genes on individuals’ immune functions; to clarify the relationship and immune mechanism between sterile inflammation and microecology imbalance; to clarify the relationship between the mucosal barrier destruction of opportunistic infections, congenital immunodeficiency or secondary immunodeficiency, among others, and the human microecology structure and function, with the focus placed on the interaction network between key microorganisms and immunity and opportunistic pathogens.
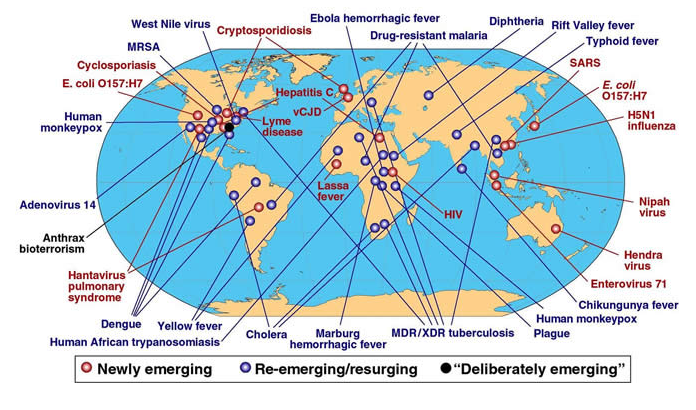
感染性疾病导致的死亡人数占全球死亡总数25%以上
II Microecology and liver diseases
The main research topics of microecology and liver diseases are to clarify the structural and functional changes of intestinal microecology in the course of the development and progression of liver diseases; to study the mechanism of intestinal microecology on host immunity, metabolism and the development and progression of liver diseases through the gut-liver axis; to screen for microecological markers or targets for early warning, diagnosis and treatment of liver diseases; to create new microecology-related technologies, new products and new strategies for the early warning, prevention, prediction, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis and rehabilitation of liver diseases.
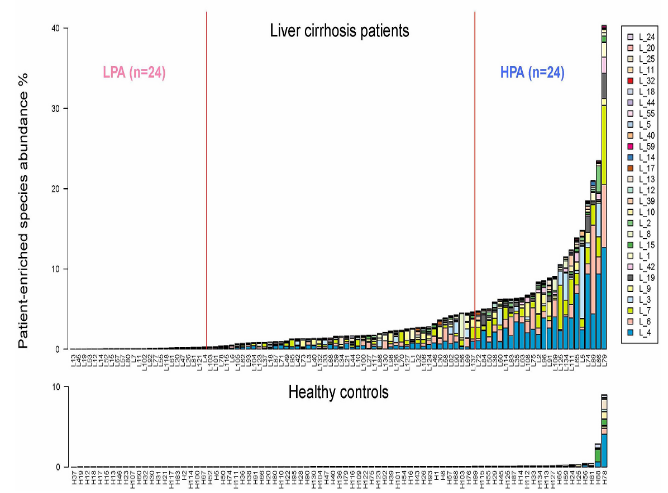
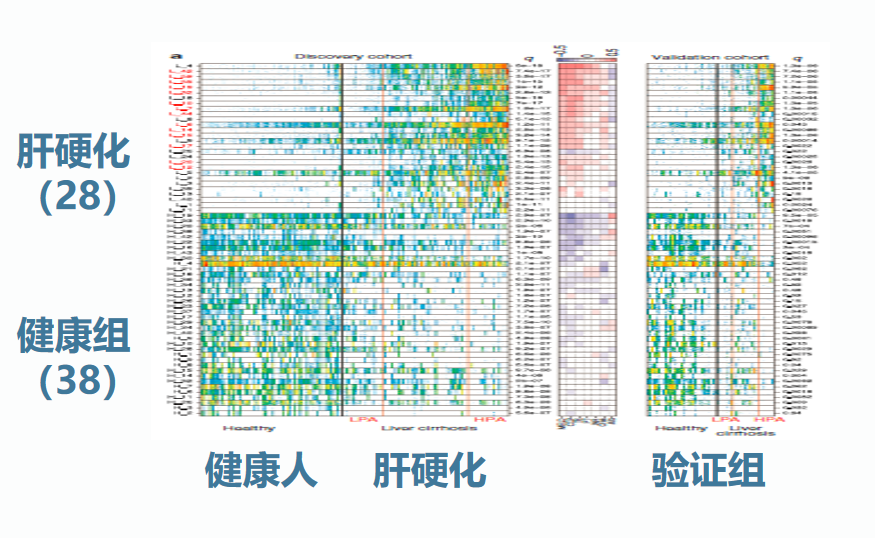
肝硬化和健康人肠道菌群的丰度变化
Qin N, et al. Nature. 2014
III Intestinal microecology and immunity to infection
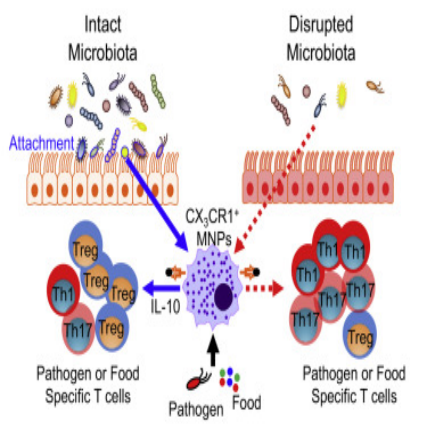
The main research topics of intestinal microecology and immunity to infection are to explore the distribution, structure and function of human microecology in infants and children, adults and the elderly, and to analyze the corresponding immune structure and function; to clarify the interaction and mechanism thereof between human microecology and immunity development, maturity and aging; to reveal the role and mechanism of important microorganisms on immune cell differentiation, distribution and migration; to study the mechanism by which important immune cells or factors regulate intestinal microecology.
IV Human mircoecology and antimicrobial resistance
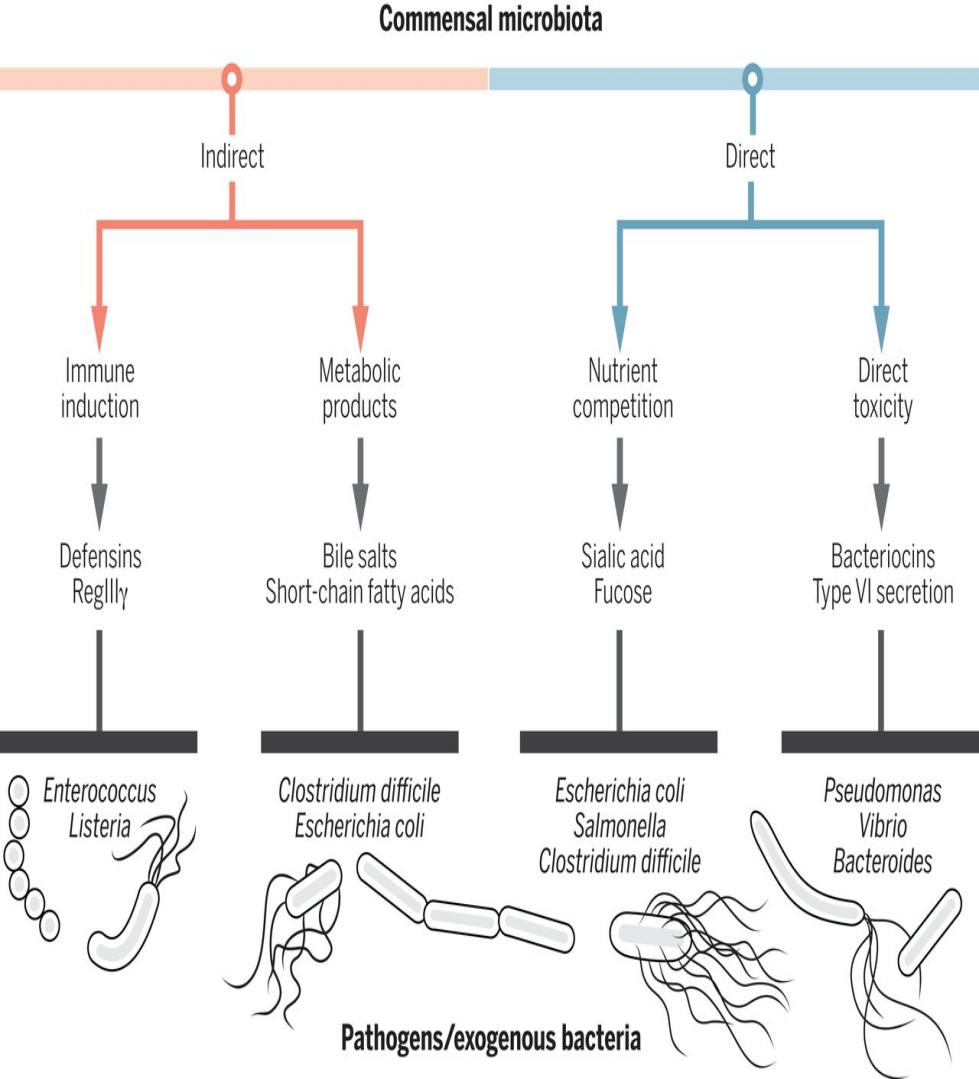
The main research topics of human microecology and drug resistance are to combine artificial intelligence, metagenomic database, cloud-based big data platforms, among others, to establish a multi-level and comprehensive antimicrobial resistance active monitoring system with the function of real-time early warning; to build a library of special and/or important drug-resistant strains, as well as a resistome library, a drug-resistant bacteria tracking system and an early warning system based on human microecological data; to conduct in-depth basic research on the occurrence, development, prevalence, evolution and mechanism of antimicrobial resistance, and clarify the intermediary mechanism of human microecology in the spread of antimicrobial resistance; to create new technologies for antimicrobial resistance diagnosis, treatment, prevention and control.
Microecology and Aging
I. Research on the age-related changes in human microecology and its correlation with aging phenotypes
The main research topics of the research on the pattern of age-related changes in human microecology and its correlation with aging phenotypes are to establish China’s first full-life-cycle microecological biobank and database, and to reveal the pattern of age-related or aging-related physiological and pathological evolution of microecology; to establish a common benchmark for national and even global human microecology research; to reveal the age-related and aging-related dynamic microecological network of human bacteria, fungi and viruses.
II Relationship and mechanism between gut microecological changes and gut-liver axis aging/ gut-brain axis aging
The main topics of the research on the relationship and mechanism between gut microecological changes and gut-liver axis aging/ gut-brain axis aging are to establish gut organoids and a (living) biobank derived from tissues of healthy people and sick people at different ages; to establish animal models for microecology and aging research; to study the relationship and mechanism between aging of the gut, liver (linked to the intestine via the gut-liver axis), and brain (linked to the intestine via the gut-brain axis) and microecological changes.
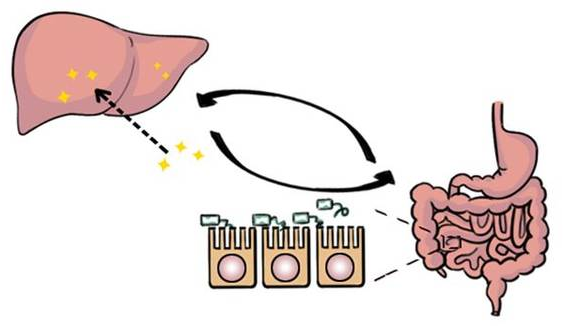
肠肝轴
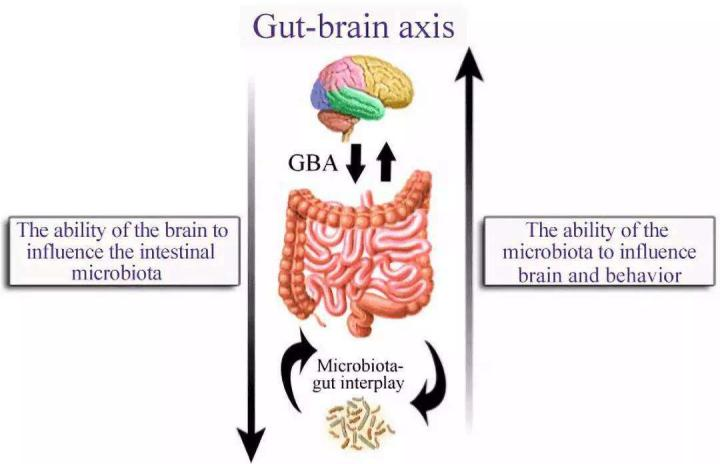
肠脑轴
III Human microecological changes in longevity families and their associations and mechanism of interaction with host genetic factors
The main topics of the research on human microecological changes in longevity families and their associations and mechanism of interaction with host genetic factors are to carry out the screening of “longevity-promoting” genes in host microorganisms; to carry out targeted screening, identification and characterization research of intestinal functional probiotics in longevity families, and study their anti-aging mechanism at the cellular and molecular levels.
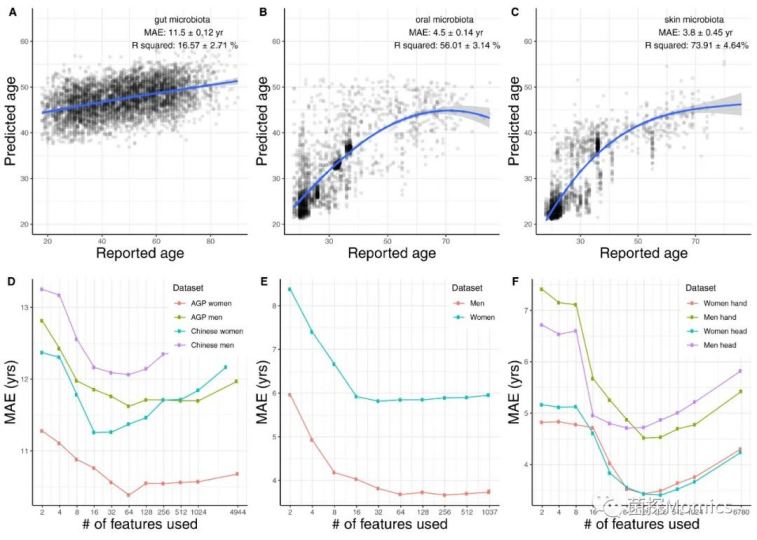
微生物可用于预测年龄
IV Research on technology and mechanism of microecological intervention to promote age-related health and prolong lifespan
The main topics of the research on the technology and mechanism of microecological intervention to promote age-related health and prolong lifespan are to formulate precise plans for overall regulation, develop technologies and products to improve age-related health and prolong lifespan; to clarify the mechanism of action of anti-aging probiotics and prebiotics; to develop a series of related food, health products, medicines and age-related strategies.
微生态抑制剂
V Research on microecology and chronic diseases
The main topics of research on microecology and chronic diseases are to reveal the structural characteristics of gut microbiota in major autoimmune and metabolic diseases; to find and screen disease-specific intestinal strains; to clarify the interaction mechanism between the gut microecology and key targets of host autoimmune and metabolic diseases; to analyze the mechanism of synergistic pathogenicity between host genetic susceptibility and human microbial homeostasis disequilibrium; to conduct research on microecological prevention and treatment of autoimmune and metabolic diseases.
VI Research on microecology and tumor
The main topics of the research on microecology and tumor research are to screen important tumor-related gut microorganisms and clarify their regulatory mechanisms on tumor occurrence and development; to study microecology-based tumor prediction, early diagnosis, intervention and therapeutic target and prognosis; to clarify the interaction and the mechanism thereof between human microecology and antitumor drug metabolism and tumor immunotherapy; to conduct R&D of new tumor prevention and treatment approaches, technologies and products based on microecology.
VII Human microecology and brain and neuropsychiatric diseases
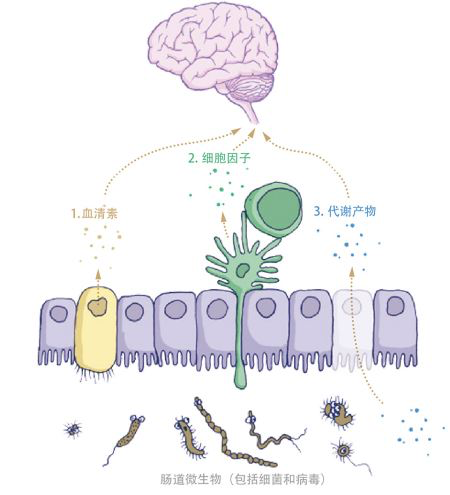
The main topics of the research on human microecology and brain and neuropsychiatric diseases are to clarify the interaction and the mechanism thereof between gut microorganisms and the susceptibility genes for brain and neuropsychiatric diseases; to explore the genetic predisposition and mechanism of gut microecology-induced brain and neuropsychiatric diseases; to develop standard diagnostic technologies and therapeutic target drugs for brain and neuropsychiatric diseases based on human microecology; to reveal the signaling pathways that psychiatric diseases regulate gut microecology through neuroendocrine and neuroimmune systems; to carry out research on early detection, early prevention and early intervention of diseases based on bacterial biomarkers.
Microecological Biomedical Technology Research
I Research and development of diagnosis and therapeutic technology in microecology
R&D of diagnosis and therapeutic technology in microecology is divided into three main areas: anti-infective microecological technology R&D, anti-aging microecological technology R&D, and microecology and chronic graft dysfunction and the technology research.
1. R&D of anti-infective microecological technology is mainly carried out in five major aspects: the establishment of a biobank and genome database for pathogenic microorganisms of infectious diseases; the development of new anti-infective resources in human microorganisms and their products; the development of human microecology-based technologies for early warning, prediction, diagnosis and course screening of infectious diseases; the creation of new anti-infective microecological regulators; and the establishment of new technologies and strategies for infection treatment based on human microecology.
2. Anti-aging microecological technology R&D is carried out in two major areas: the exploration of anti-aging strategies and drug targets; the development of intervention strategies, new technologies and products for delaying aging.
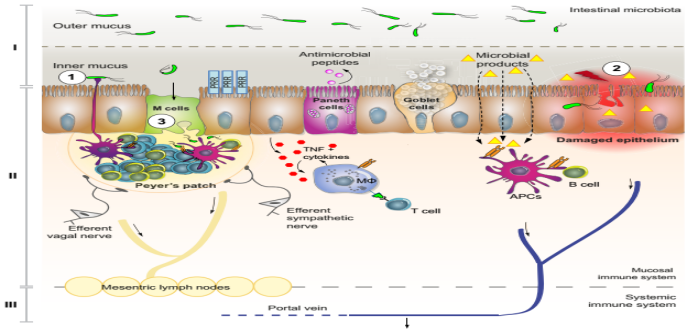
3. Research on microecology and chronic graft dysfunction and relevant technologies is carried out in three major aspects: studies on the characteristics of changes in immune response effect and immuno-regulatory mechanisms due to intestinal microbiota imbalance after transplantation; clarifications on the effects of immune microecology and intestinal microecology on the recurrence of hepatitis B/liver cancer and investigations on the molecular mechanism of its recurrence and metastasis; the exploration of new intervention methods and individualized solutions to prevent and treat opportunistic infections in the immune tolerance state after liver transplantation.
II Organ transplantation and regenerative medicine research
Organ transplantation and regenerative medicine research mainly consists of four areas: organ transplantation research, organ support research, tissue and organ regeneration research, reproductive assistance and embryo cryopreservation and transplantation research.
1. Organ transplantation research is carried out in three major areas: the establishment and industrialization of an ex vivo/isolated mechanical perfusion-for-repair platform and a new organ preservation system; research on the genetically modified mini-pigs as organ donors for xenotransplantation; and the screening and establishment of reasonable immunosuppression protocols.
2. Organ support research focuses on two major areas: the use of technologies such as 3D printing and artificial blood vessels to build regenerative or invasive artificial livers; and the exploration of co-culture systems for renal organoids and vascular organoids to create bioartificial kidneys.
3. Research on tissue and organ regeneration is carried out in three major domains: the construction of tissue-engineered nerves based on mechanisms of nerve regeneration, degeneration, injury repair and functional reconstruction; the research and development of new biomaterials for regeneration with independent intellectual property rights; and the application of cell transplantation to assist the regeneration and repair of large organs.
4. Research on reproductive assistance and embryo cryopreservation and transplantation mainly focuses on two areas: improving the in vitro culture medium, culture environment and culture technology to increase the fertilization rate of oocytes and the rate of superior quality embryos; reconstructing an intact uterine environment in vitro to assemble non-human primate embryos.

III. Research on modern biomedical technologies
The five major topics of modern biomedical technology research are: innovative vaccines, tumor vaccines, tumor biotherapy, nanomedicine technology and anti-aging, Internet+ and artificial intelligence for chronic disease management.
1. Research on innovative vaccines is carried out in two main areas: multi-dimensional research on the design of innovative vaccines based on pathogen biology, structural biology, and information biology; cultivation of innovative vaccine seed strains in various ways and the establishment of a vaccine R&D technology system.
2. Research on tumor vaccines is mainly carried out in three aspects: research on new clinical genome editing therapies; modification and optimization of CAR-T therapies; using NK and other immune cells and stem cells to establish individualized and precision T-cell therapies.
3. Research on tumor biotherapy mainly aims to design antibody therapeutic drugs based on the study of novel oncogenic sites at the cellular and molecular level, activate the patient’s own immune system and prevent the growth, spread and recurrence of tumors.
4. Research on nanomedicine technology and anti-aging is carried out in two main areas: research on the precise delivery of contrast agents, diagnostic reagents or drugs based on nanoscale particles; research on micro-nano robotics.
5. Research on Internet+ and artificial intelligence for chronic disease management focuses on two main areas: the development of portable mobile medical devices for disease prediction and prognosis; the establishment of an efficient, simple, and convenient Internet+ platform for chronic disease follow-up of cardiovascular diseases.