Recently, academician Li Lanjuan, director of the laboratory, microecological engineering laboratory Lv Longxian assistant researcher team, "Food&Function" magazine published entitled "Akkermansia muciniphila attenuated lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by modulating the gut microbiota and SCFAs in mice".
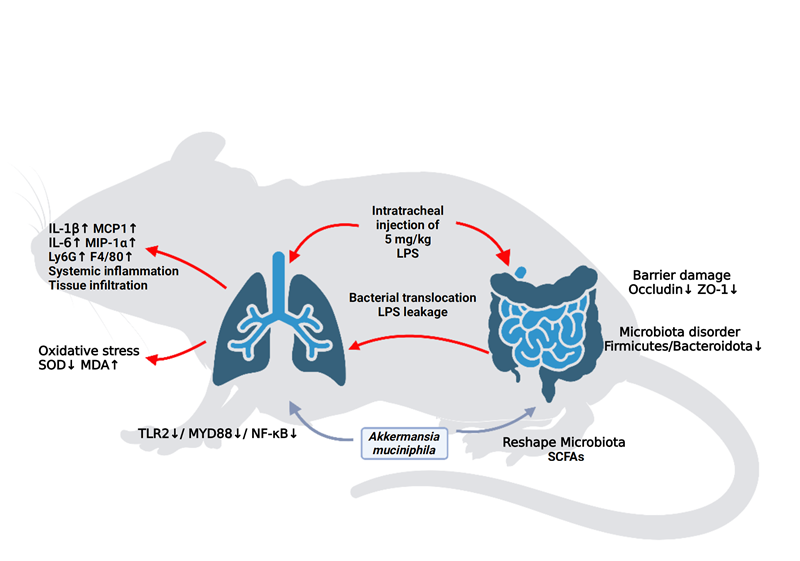
Aiming at the close association between the imbalance of intestinal flora and severe respiratory syndrome and acute lung injury (ALI) found in clinical practice, the team carried out a basic research based on the modulation of the gut microbiota to alleviate the lung injury by relying on the probiotic resource library and using probiotic interventions in conjunction with the ALI model. At the molecular level, the team found that the intervention of mucinophilic Ackermannia (Akk) could effectively reduce the tissue damage of lung injury, and significantly reduced the oxidative stress and inflammatory response induced by bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), lowered the level of myeloperoxidase (MDA), enhanced the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), lowered the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and decreased the macrophage and neutrophil infiltration. In addition, Akk maintained intestinal barrier function, remodelled disturbed microbial communities and promoted secretion of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs).Akk intervention significantly down-regulated the expression of TLR2, MyD88 and NF-κB. In addition, butyrate supplementation significantly improved the inflammatory response and attenuated histopathological damage in ALI mice, thereby restoring the intestinal butyrate concentration. This demonstrated that the intestinal flora could regulate lung health through the gut-lung axis, elucidated the principle of intestinal microecology under Akk intervention to alleviate acute lung injury, and provided a theoretical basis for the application of intestinal microecological agents in the health industry.
Shen Jian is the first author of this paper, and Lanjuan Li is the corresponding author. This project was supported by the Major Special Project of Shandong Laboratory (SYS202202) and Jinan Microecology Biomedical Shandong Laboratory (JNL-2022001A).